
game
From Zero to Retail Hero – Your First Week in Discounty
Starting Discounty feels overwhelming. You ve got [ ]

Technology
U4GM Diablo 4 Items: Browse Lair Boss Keys, Runes, Elixirs & More
Diablo 4 is an action game in which players need to kil [ ]
Technology
How Pippit’s AI Presentation Maker is Revolutionizing Business Pitches in 2025
The year 2025 brings a complete transformation to how b [ ]
Technology
Win Full-Bright Scholarship With Gauth Personal Statement Writer
It is the dream of any student to successfully apply fo [ ]

Lifestyle
Ferrero Rocher Bulk – Navigating Minimum Order Quantities & Pricing
Beyond mere pleasure, Ferrero Rocher s attraction [ ]

Business
Selecting Raw Materials for Supplement Manufacturing
The quality and efficacy of a dietary supplement hinge [ ]
Lifestyle
Creating Gothic Art Descriptions Made Easy with Gauth
Gothic art is very detailed and has strong contrasts an [ ]

Technology
Enlisting the Possible Causes of Compressed Air Leakage
The most common issue in most compressed air systems is [ ]

Technology
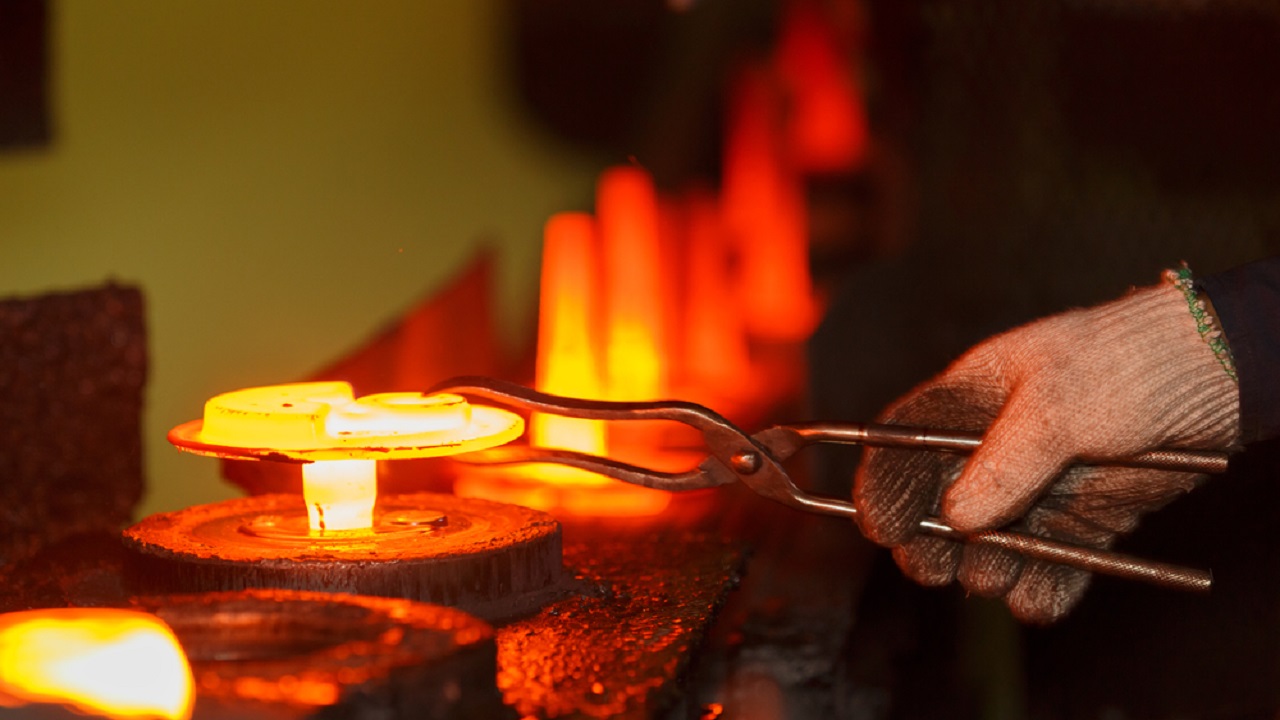
Future Trends in Hot Die Forging: What to Expect
Hot die forging has long been a cornerstone in the manu [ ]

Technology
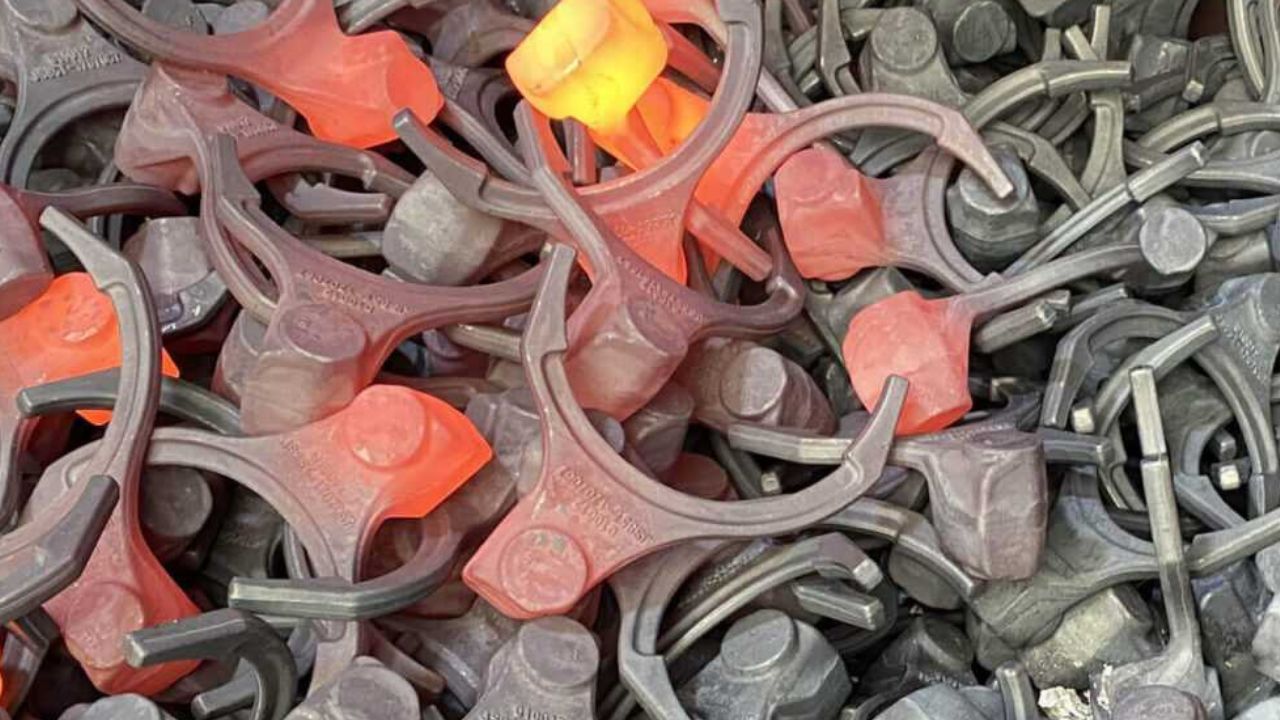
Visit the Homepage for Obtaining Details about the Forging Process
The vast majority of metals can be produced and fabrica [ ]

Technology
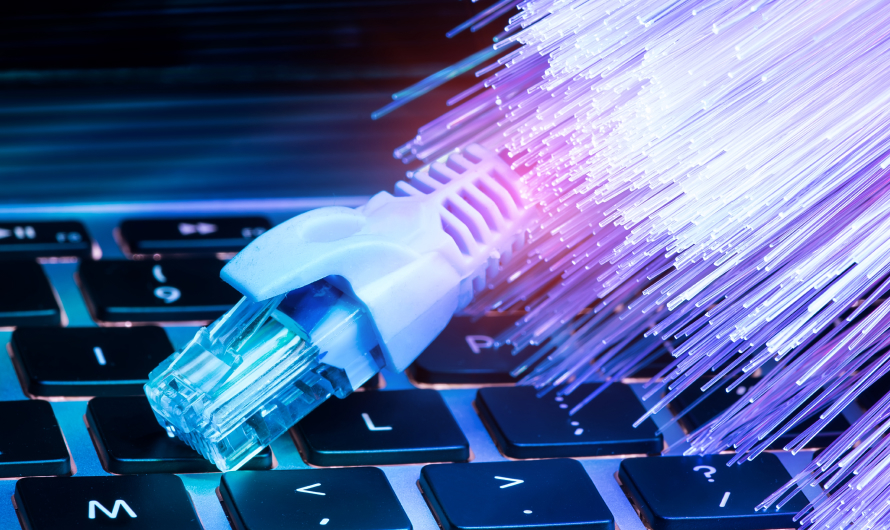
The Future of Fiber Optics and Its Endless Possibilities for Connectivity
Technology is continuously evolving, and the future loo [ ]

Technology
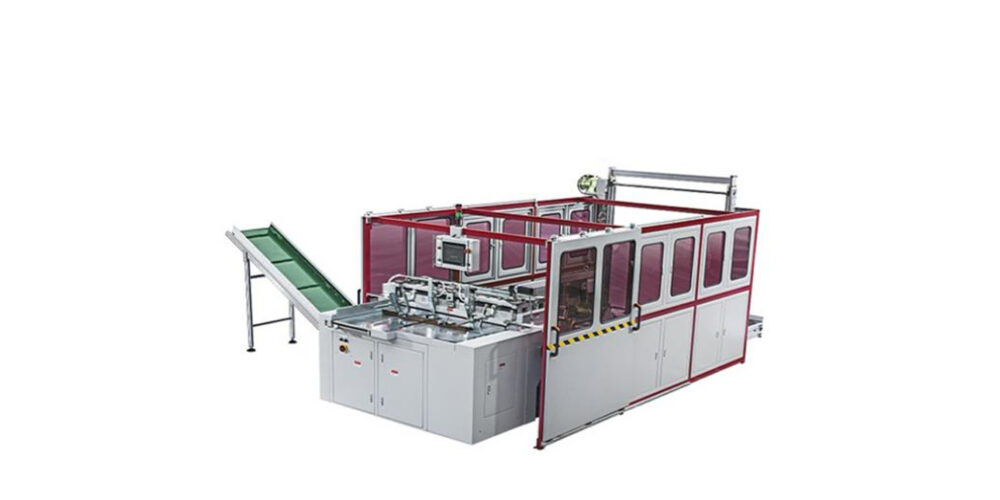
Get The Detail About the Best Case Making Manufacturers In The Market!
The Internet has developed so much that the work that n [ ]
